Semi truck protection equipment requires systematic maintenance to deliver reliable performance when facing road hazards. Properly maintained truck guards and truck guard maintenance protocols ensure equipment functions effectively against wildlife collisions, road debris impacts, and vehicle accidents that threaten expensive repairs and operational downtime.
Fleet operators and owner-operators who maintain consistent inspection and care routines significantly reduce equipment failures and extend guard service life. Professional maintenance approaches prevent minor issues from developing into major problems that compromise operational safety and equipment performance.
Effective truck guard maintenance programs incorporate daily inspection protocols, seasonal maintenance schedules, failure pattern recognition, and comprehensive documentation systems. This systematic approach ensures maximum protection when encountering animals, debris, or collision situations on highways and industrial routes.
Daily Inspection Protocols
Daily pre-trip inspections form the foundation of effective truck guard maintenance programs. These inspections identify damage, wear, and mounting issues before they compromise protection capabilities during encounters with wildlife, road debris, or collision situations.
Systematic visual inspection covers all guard components and mounting hardware with particular attention to high-stress areas. Focus areas include structural integrity, mounting point security, and component alignment that affects protection performance.
Professional inspection procedures begin with an overall visual assessment followed by detailed component examination. Check mounting brackets for signs of stress, fatigue, or movement that could indicate developing failures. Inspect guard surfaces for impact damage, cracks, or deformation that might compromise structural integrity.
Essential daily inspection elements:
- Visual examination of all welds and structural joints for cracks or separation
- Hardware inspection focusing on bolt tightness and mounting bracket integrity
- Alignment verification, ensuring guards maintain proper positioning and coverage
- Impact damage assessment from encounters with animals, debris, or minor collisions
- Component movement testing to identify loose mounting points or structural issues
- Surface condition evaluation, including protective coating integrity and corrosion signs
Complete daily inspections require around 1-2 minutes and integrate seamlessly with standard pre-trip routines. Consistent execution identifies developing problems before they affect guard performance during critical protection situations.
Failure Pattern Recognition
Understanding standard failure modes enables early problem identification and prevents guard failure during critical protection situations. Most truck guard maintenance issues follow predictable patterns that experienced operators learn to recognize quickly.
Mounting point stress represents the most frequent failure mode affecting all guard types. Constant road vibration combined with impact loads from animals, debris, and minor collisions creates fatigue at connection points. Early detection involves monitoring for enlarged bolt holes, cracked mounting plates, and unusual guard movement.
Structural fatigue typically develops at high-stress points, including weld joints and impact zones. Different guard designs exhibit characteristic failure patterns:
Aero truck guards often show stress at aerodynamic transition areas where streamlined sections meet structural components. These guards may develop cracks at the leading edge connections.
Defender models may develop issues at reinforcement connection points where structural elements integrate with primary frameworks. Fully enclosed uprights can show stress at base connections.
Texas bumpers commonly experience wear at lower impact edges where animal and debris contact occurs most frequently. These guards may show fatigue at latch mechanism mounting points.
Impact damage patterns vary by collision type and severity. Animal strikes create focused damage at contact points while debris impacts often cause surface damage with possible underlying structural effects.
Critical warning indicators:
- Unusual operational noises, including rattling, grinding, or impact sounds
- Visible guard movement beyond normal parameters or excessive deflection
- Alignment changes, gaps between components, or asymmetrical positioning
- Handling characteristics changes, increased vibration, or steering effects
- Hardware loosening patterns, repeated fastener failures, or mounting deterioration
Repair Procedures and Standards
Professional repair procedures ensure truck guard maintenance work meets performance standards and maintains equipment reliability under operational stresses. Proper repair techniques prevent recurring problems and maintain warranty coverage while ensuring continued protection capabilities.
Hardware replacement requires strict adherence to manufacturer specifications, including torque values, fastener grades, and installation procedures. Standard hardware substitutions often fail under operational loads from animal impacts, debris strikes, or collision forces. Using incorrect fasteners can void warranty protection and create liability issues.
Welding repairs demand specific expertise and procedures appropriate for guard materials, stress conditions, and operational requirements. Different aluminum alloys require specialized welding techniques and filler materials to maintain structural integrity. Steel components need proper heat treatment and stress relief procedures to prevent brittle failure zones.
Structural repairs must address root causes rather than symptoms to prevent recurring failures. Simply reinforcing damaged areas without correcting underlying stress concentrations often leads to failure migration and progressive structural deterioration.
Professional repair documentation includes:
- Detailed damage assessment with photographic records showing the extent and severity
- Repair procedures performed, including materials, specifications, and quality control measures
- Hardware replacement records with torque specifications, fastener grades, and installation verification
- Completion inspection results, performance verification, and warranty impact assessment
- Operator training updates and maintenance schedule adjustments based on repair findings
Quality control procedures verify repair integrity before returning equipment to service.
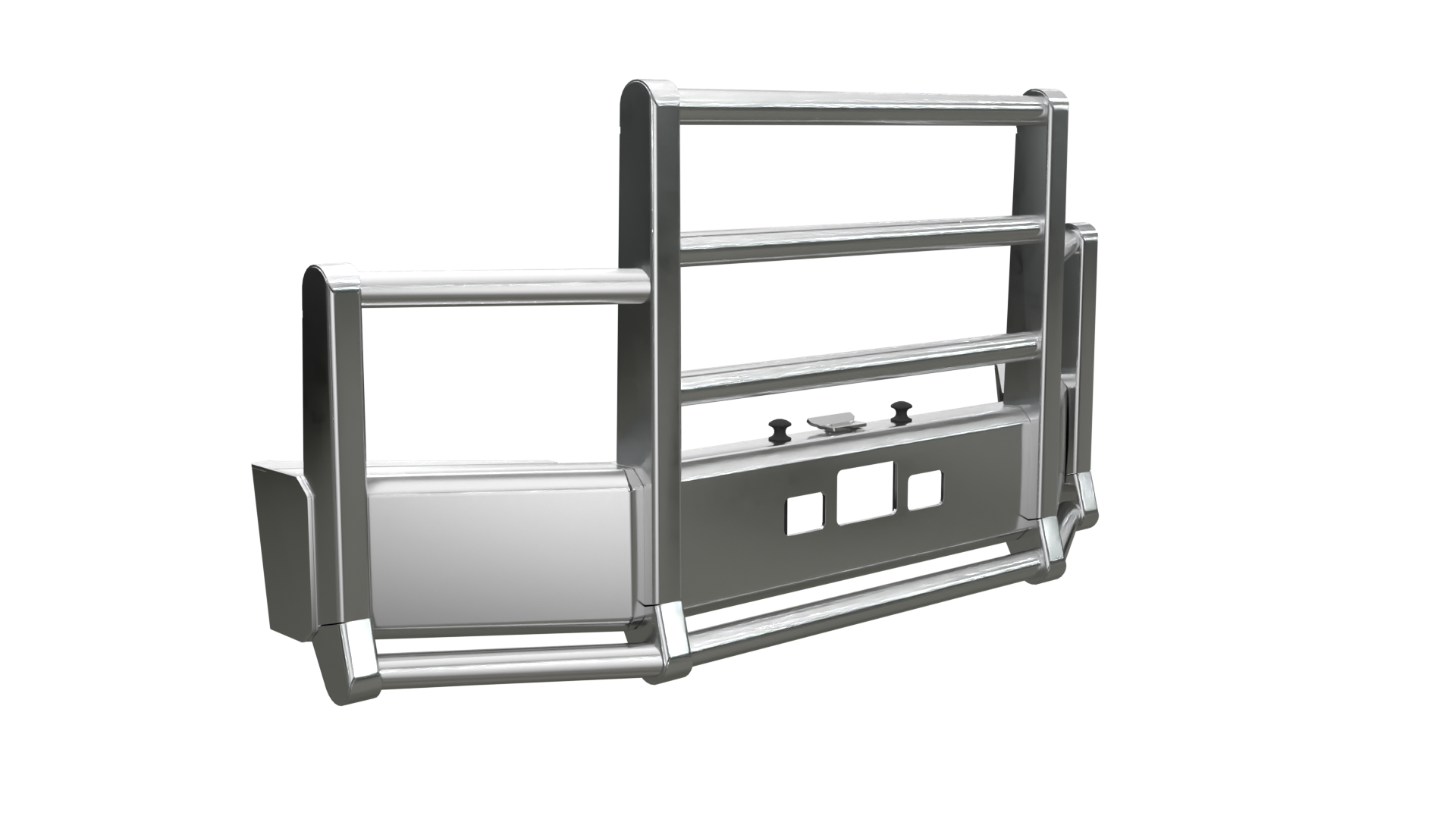

Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Proactive truck guard maintenance prevents problems through systematic care and component protection strategies. Preventive approaches reduce repair frequency, extend equipment service life, and maintain optimal protection performance when encountering animals, debris, or collision situations.
Regular cleaning removes corrosive materials and enables thorough inspection during routine maintenance procedures. Weekly cleaning schedules prevent material accumulation that obscures developing problems and accelerates component deterioration. Proper cleaning techniques preserve protective coatings while removing road salt, mud, and debris that can cause premature failure.
Protective treatments, including specialized coatings and corrosion inhibitors, extend equipment life in harsh operating environments. A professional application ensures proper coverage and maximum effectiveness against environmental threats. These treatments require periodic renewal based on operating conditions and exposure levels.
Hardware upgrades address known failure points with improved components designed for enhanced durability. Upgrading to higher-grade fasteners, adding thread-locking compounds, or installing vibration-resistant hardware prevents recurring loosening problems without compromising original design integrity.
Lubrication programs maintain moving components, including latch mechanisms, pivot points, and adjustment hardware. Proper lubrication reduces wear, prevents corrosion, and ensures reliable operation during critical protection events.
Operating environment considerations significantly affect preventive maintenance requirements. Equipment operating in construction zones faces increased debris impact risks. Wildlife areas present animal collision hazards that demand enhanced structural inspections. High-debris environments benefit from increased cleaning frequency and protective coating renewal.
Environmental factors influencing maintenance include:
- Construction zone operations requiring enhanced debris protection and frequent cleaning
- Wildlife corridor routes demanding structural integrity verification and impact damage assessment
- Industrial environments with chemical exposure require specialized protective treatments
- High-mileage operations need accelerated inspection schedules and component replacement
- Off road use, such as logging and oil patch work, would also influence maintenance routines
Documentation and Record Systems
Comprehensive maintenance records enable pattern analysis and predictive maintenance scheduling for optimal equipment performance. Effective truck guard maintenance programs rely on detailed documentation to optimize service intervals, identify recurring issues, and support warranty claims.
Maintenance records should document all inspection results, repairs performed, component replacements, and environmental factors affecting equipment performance. Photographic documentation provides visual reference for damage patterns, assessment of repair quality, and training purposes.
Digital record systems enable trend analysis and predictive maintenance scheduling. Modern fleet management systems can integrate guard maintenance data with vehicle maintenance records for comprehensive asset management. Electronic records facilitate warranty claims and enable rapid access to maintenance history during equipment evaluation.
Essential documentation elements:
- Inspection dates with mileage, operating hours, and environmental conditions recorded
- Damage descriptions with severity assessment, photographic documentation, and cause analysis
- Repair procedures with materials, specifications, completion verification, and quality control results
- Component replacement records, including part numbers, supplier information, and installation verification
- Operating conditions, route characteristics, and environmental factors affecting equipment performance
Record retention policies should align with warranty periods and regulatory requirements. Most manufacturers require maintenance documentation for warranty claims, while regulatory agencies may require safety-related maintenance records for compliance verification.
Training programs ensure maintenance personnel understand proper procedures, documentation requirements, and safety protocols. Regular training updates address new equipment features, revised procedures, and lessons learned from maintenance experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should truck guards undergo a detailed maintenance inspection?
Daily visual inspections during pre-trip procedures identify immediate issues, while detailed inspections should occur weekly for high-mileage operations or monthly for standard highway applications. Seasonal comprehensive evaluations help identify wear patterns and plan preventive maintenance effectively.
What indicates immediate attention requirements for truck guard systems?
Critical indicators include loose or missing mounting hardware, visible structural cracks, unusual operational noises, and guard misalignment. Any damage affecting structural integrity or mounting security requires immediate professional evaluation before continued operation.
Can maintenance be performed using standard shop equipment and procedures?
Basic maintenance, including cleaning, hardware tightening, and surface treatment, can be performed with standard equipment by trained personnel. Structural repairs, welding work, and component replacement typically require specialized equipment and expertise for reliable results and warranty compliance.
When should truck guards be replaced rather than repaired?
Replacement becomes necessary when structural damage compromises guard integrity, when repair costs approach replacement costs, or when repeated failures occur at the exact location. Guards with extensive corrosion, multiple structural repairs, or compromised mounting points typically require replacement.
What maintenance records are essential for truck guard warranty compliance?
Complete documentation, including inspection dates, repair procedures, component replacements, and operating conditions, maintains warranty coverage. Photographic records of damage and repairs provide additional support for warranty claims and help identify patterns affecting equipment performance.
Maintain peak protection performance with professional maintenance programs. Contact HERD for maintenance guidelines specific to equipment configurations and operating environments.